Opini
Jihad Melawan Kekerasan Seksual
Published
10 years agoon
By
Mitra Wacana

Wahyu Tanoto
Oleh Wahyu Tanoto
Masih segar dalam ingatan kita peristiwa kekerasan seksual di Jakarta International School (JIS), negeri ini kembali dibuat gempar dengan peristiwa serupa. Namun, kali ini peristiwa tersebut terjadi di daerah; tepatnya di kabupaten Banyumas dengan terduga pelaku adalah penjual cilok keliling bernama Dedi Santoso (25) dengan korban yang mencapai 28 anak, dengan rentang usia antara 10 hingga 14 tahun, seperti dilansir harianterbit.com (6/6).
Peristiwa ini semakin mendesakkan kepada kita; orangtua, praktisi pendidikan, praktisi kesehatan, praktisi hukum, aktivis LSM, instansi pemerintah serta masyarakat umum, betapa pentingnya pendidikan kewaspadaan sejak dini untuk selalu mengingatkan kepada kita selalu mawas dan mengindahkan kejadian sekecil apapun di lingkungan sekitar.
Pengalaman telah memberikan pelajarn berharga, bahwa pada beberapa peristiwa kekerasan seksual, biasanya korban cenderung sulit bahkan sama sekali tidak dapat melapor; tidak bersedia melapor, tidak mengerti proses pelaporan, takut, malu, diancam, diintimidasi, di stigma atau bahkan upaya mencari informasi tentang akses terhadap proses-proses peradilan hukum yang belum dipahami secara lengkap, dapat menyebabkan semakin bertambahnya tantangan dalam upaya penyelesaian berbagai persoalan kekerasan, terutama berkaitan dengan kekerasan seksual terhadap anak.
Masih lemahnya keamanan, penjagaan bagi anak-anak yang berada di ruang publik, minimnya akses peradilan hukum yang terjangkau bagi korban untuk menuntut, serta kondisi sosial-ekonomi-budaya masyarakat menjadi tantangan-tantangan besar bagi anak-anak yang seolah terus mengiringinya. Lebih miris lagi masih adanya stigma yang kerap menjadi julukan baru bagi korban kekerasan seksual, mau tidak mau semakin menjadi beban psikis yang mesti ditanggung selama hidup.
Perlakuan yang mensudutkan, mencaci/mengejek, merendahkan, menggunjing bahkan mensalahkan korban tidak jarang dapat kita saksikan dengan jelas serta tergambar melalui pemberitaan di pelbagai media. Korban kekerasan seksual terhadap anak dalam konteks ini, mau tidak mau harus melalui proses yang begitu rumit, melelahkan ditambah lagi sistem penanganan yang masih belum ramah, terlebih pengetahuan mengenai issu seksualitas relatif belum lengkap dan benar serta tepat, dianggap tabu, atau bahkan tertutup sama sekali untuk di perbincangkan karena masih dianggap “aib” yang harus ditutupi meskipun di tengah masyarakat yang “mengaku” sudah demokratis.
Persoalan tersebut, semakin mengemuka dan kompleks manakala informasi mengenai kesehatan seksual dan Reproduksi (KSR) bagi anak, remaja/pelajar sekolah menengah yang belum berkelanjutan sehingga masyarakat dan anak muda pada umumnya harus mencari sendiri informasi tentang kesehatan seksual dan reproduksi Reproduksi (KSR) melalui teman sebaya, melalui media online/internet yang relative mudah di capai dengan catatan tingkat keakuratannya perlu diperhatikan dan informasi yang tersedia belum komprehensif.
Oleh karenanya, minimal dibutuhkan dua hal untuk mensikapi peristiwa kekerasan sekual terhadap anak yang terus terulang. Pertama dalam level konseptual, Negara melalui pemerintah dan jajarannya perlu mensediakan lebih banyak lagi infrastruktur pendukung untuk melakukan pencegahan, penanganan serta pemulihan survivor (korban) kekerasan seksual yang lebih sesuai dengan standar perlindungan bagi korban.
Dalam konteks ini keberadaan Pusat Pelayanan Terpadu Perlindungan Perempuan dan Anak (P2ATP2A) di setiap daerah perlu di optimalkan kembali. Jika diperlukan, keberadaan P2TP2A ini ada di setiap desa bahkan RT, dengan beranggotakan masyarakat setempat yang diperkuat dukungan anggaran dari pemerintah desa atau sekurang-kurangnya setiap P2TP2A di daerah memiliki rencana strategis atau road map (peta jalan) dalam menjalankan fungsinya sebagai lembaga yang memiliki kewenangan khusus melakukan perlindungan. Lebih lanjut, program nasional mengenai kota layak anak perlu dipercepat untuk pembangunan infrastruktur pendukungnya; baik aturan ataupun aparatnya.
Sedangkan di level nasional melalui Kementerian Pendidikan Nasional dan Kebudayaan, sudah seharusnya memastikan aturan dan pelaksanaan pendidikan gender, HAM, hak kesehatan seksual dan reproduksi (kespro) bagi guru maupun siswa muali dari tingkat dasar hingga Perguruan Tinggi, demi menciptakan generasi yang sadar dan adil gender serta memahami persoalan kesehatan seksual dan reproduksi sebagai cikal bakal pembangunan manusia yang anti kekerasan dan lebih luas lagi sesungguhnya sebagai upaya untuk mengeliminasi angka kekerasan seksual yang cenderung meningkat.
Kedua, dalam level operasional perlu melakukan kerjasama dengan masyarakat sipil dan organisasi/lembaga pendampingan korban, dengan aparat hukum dan kepolisian bagi perlindungan dan keamanan yang lengkap bagi anak-anak yang berada di ruang publik. Selanjutnya perlu memperbesar dan memperkuat dukungan terhadap lembaga-lembaga yang selama ini telah melakukan kerja pendampingan dan pengorganisasian di tingkat masyarakat (komunitas), baik dengan cara memperkuat kerjasama pelaksanaan agenda program, maupun dukungan financial mengingat begitu kompleksitas dan kecenderungan terulangnya peristiwa kekerasan seksual.
Opini
25 Juta Jiwa Jadi Korban Perdagangan manusia
Published
3 weeks agoon
27 March 2024By
Mitra Wacana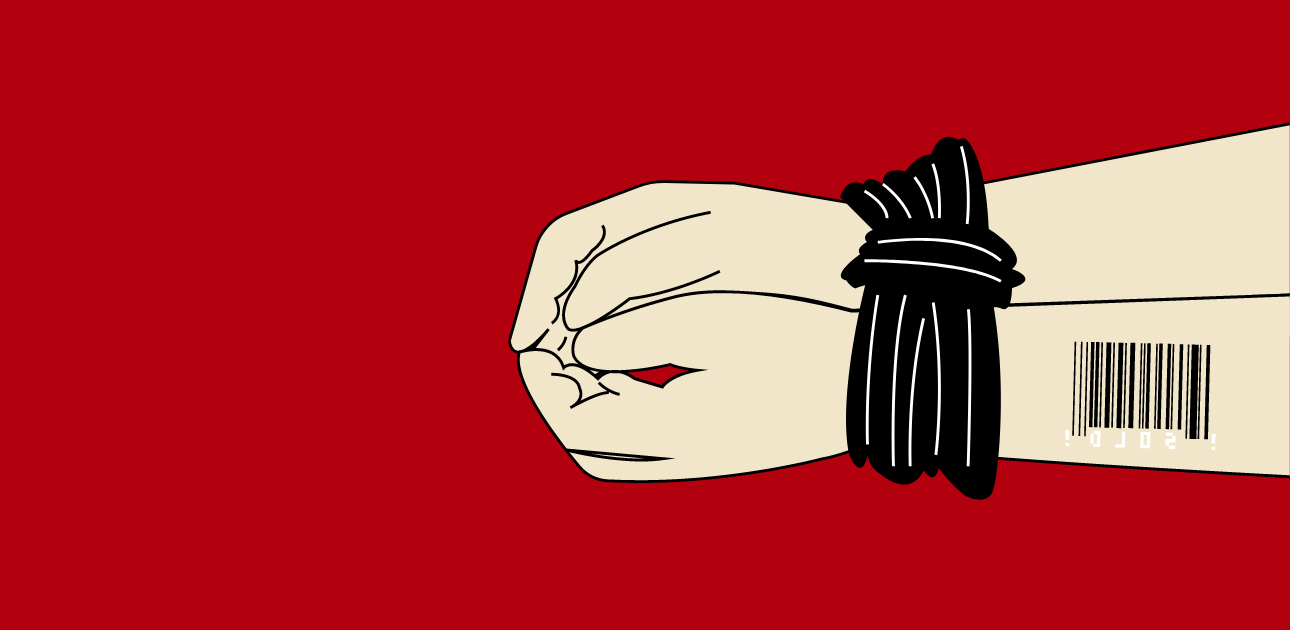

Wahyu Tanoto
Oleh Wahyu Tanoto
Perdagangan manusia adalah bentuk pelanggaran hak asasi manusia yang maha serius dan bersifat global. Menurut Perserikatan Bangsa-Bangsa (PBB), perdagangan manusia adalah “perekrutan, pengangkutan, pemindahan, penyembunyian atau penerimaan seseorang dengan cara seperti ancaman atau penggunaan kekerasan atau bentuk lainnya. Pemaksaan, penculikan, penipuan atau penipuan untuk tujuan eksploitasi.” Eksploitasi tersebut dapat berupa kerja paksa, perbudakan, pelacuran, atau bentuk-bentuk eksploitasi seksual lainnya.
Rumit dan Multidimensi
Perdagangan manusia adalah masalah yang terbilang rumit dan multidimensi. Pelakunya boleh jadi berasal dari berbagai latar belakang, termasuk individu, kelompok, atau bahkan organisasi. Korban perdagangan manusia juga berasal dari berbagai latar belakang, termasuk laki-laki, perempuan, dan anak-anak.
Merujuk United Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) dan International Labour Office (ILO), terdapat hampir 25 juta korban; perempuan, laki-laki dan anak-anak di seluruh dunia untuk tujuan eksploitasi seksual dan kerja paksa. Karenanya, perdagangan manusia merupakan pelanggaran berat terhadap martabat manusia dan menargetkan kelompok rentan seperti migran, serta pengungsi pada khususnya. Salah satu tren yang paling memprihatinkan adalah meningkatnya jumlah anak-anak yang menjadi korban, meningkat tiga kali lipat dalam 15 tahun. Kejahatan ini dilaporkan menghasilkan lebih dari $150 miliar per tahun di seluruh dunia. Hal ini semakin dianggap sebagai masalah keamanan global karena memicu korupsi, migrasi tidak teratur, dan terorisme.
Pada 2023, Indonesia masih dihadapkan dengan tantangan besar dalam mengatasi kasus Tindak Pidana Perdagangan manusia (TPPO). Menurut data yang dihimpun oleh Sistem Informasi Online Perlindungan Perempuan dan Anak (SIMFONI PPA), mencatat dari tahun 2020 sampai dengan tahun 2022, terdapat 1.418 kasus dan 1.581 korban TPPO yang dilaporkan. Dari data tersebut menunjukkan sebanyak 96% korban perdagangan orang adalah perempuan dan anak
Bahkan, yang paling gres sebanyak 1.047 mahasiswa dari 33 universitas di Indonesia diduga menjadi korban eksploitasi kerja dengan modus magang di Jerman (ferienjob) pada Oktober sampai Desember 2023. Diadaptasi dari Tempo.co, perihal kronologi kejadiannya, para mahasiswa mendapat sosialisasi dari CVGEN dan PT. SHB. Mereka dibebankan biaya pendaftaran sebesar Rp 150.000, dan membayar 150 Euro untuk membuat LOA (Letter of Acceptance).
Dampak yang mengerikan
Perdagangan manusia memiliki dampak yang menghancurkan bagi korban. Mereka, para korban perdagangan manusia kerapkali mengalami kekerasan fisik, psikologis, seksual (termasuk di ranah luring). Mereka juga mengalami kerugian ekonomi dan sosial.
Meskipun perdagangan manusia merupakan masalah yang bersifat global, namun, hal ini sering kali terlupakan dan luput dari perhatian. Ada beberapa faktor yang berkontribusi terhadap ketidaktahuan masyarakat tentang perdagangan manusia, termasuk: (1) Perdagangan manusia sering terjadi di belakang layar dan sulit dideteksi; (2) Korban perdagangan manusia kerap takut untuk bersuara dan melapor; (3) Masyarakat sering tidak menyadari bahwa perdagangan manusia sebagai masalah serius yang bisa menimpa siapa saja; (4) Peraturan perundangan-undangan dan kebijakan belum sepenuhnya dipahami oleh semua lapisan masyarakat, dan (5) Bentuk dan upaya pencegahan biasanya dianggap seremonial.
Upaya Negara
Untuk mengatasi masalah perdagangan manusia, diperlukan upaya dari berbagai pihak, termasuk pemerintah, lembaga internasional, organisasi non-pemerintah, dan masyarakat umum. Upaya-upaya tersebut diantaranya mencakup: 1) Peningkatan kesadaran masyarakat tentang perdagangan manusia, 2) Peningkatan dukungan bagi korban perdagangan manusia. 3) Peningkatan upaya penegakan hukum untuk memerangi perdagangan manusia.
Sebagaimana diketahui, pemerintah Indonesia telah mengambil langkah-langkah untuk menangani masalah perdagangan manusia. Indonesia menetapkan Undang-Undang No. 21 Tahun 2007 tentang Pemberantasan Tindak Pidana Perdagangan manusia. Undang-undang tersebut didukung oleh pembentukan Gugus Tugas Pencegahan dan Penanganan Tindak Pidana Perdagangan manusia melalui ditetapkannya Peraturan Presiden No. 69 Tahun 2008.
Meskipun begitu, masih banyak hal yang perlu dilakukan untuk mengatasi masalah perdagangan manusia di Indonesia. Pemerintah memiliki kewajiban mengoptimalkan pencegahan, pemantauan berkala, mengimplementasikan penegakan hukum, dan berkolaborasi dengan warga masyarakat demi meningkatnya kesadaran tentang kerentanan, bahaya dan dampak perdagangan manusia. Hadirnya organisasi masyarakat sipil yang konsen terhadap isu perdagangan manusia memang relatif belum massif, namun, pemerintah perlu memberikan apresiasi terhadap mereka yang telah berkontribusi-memiliki kepedulian-untuk memerangi perdagangan orang. ***











